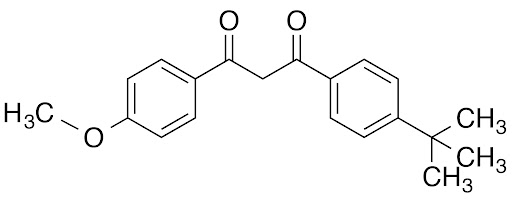
Avobenzone (Butyl Methoxydibenzoylmethane)
What Is Avobenzone?
Avobenzone is an oil-soluble, synthetic chemical sunscreen filter belonging to the dibenzoylmethane class. It is known for providing strong protection across the entire UVA spectrum (310–400 nm), including both UVA I and UVA II. It is the only globally approved UVA filter available in the United States, making it a critical component in many broad-spectrum sunscreen formulations.
Also listed by its INCI name Butyl Methoxydibenzoylmethane, avobenzone has been FDA-approved since 1988 and is considered the gold standard for UVA protection in many regions due to its ability to absorb long-wave UVA rays, which are most strongly linked to photoaging and pigmentation.
How It Works
Avobenzone functions as a UV absorber, converting harmful ultraviolet radiation into less damaging infrared radiation (heat), thereby protecting the skin at a cellular level.
While highly effective in blocking UVA radiation, avobenzone has a critical drawback: it is not photostable. When exposed to sunlight, it undergoes rapid photodegradation — losing up to 50–90% of its UV-filtering ability within 1 hour if used alone. This photodegradation not only reduces its effectiveness but can also generate free radicals, which may contribute to oxidative stress.
To stabilize avobenzone in formulations, it is typically combined with ingredients like Tinosorb S, Octocrylene, or encapsulated in nanocarriers such as mesoporous silica microparticles. These strategies enhance its UV stability and reduce its penetration into the deeper layers of skin.
Key Specifications
- Structure: C₂₀H₂₂O₃
- Chemical Class: Dibenzoylmethane derivative
- IUPAC Name: 1-[4-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)phenyl]-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)propane-1,3-dione
- Molecular Weight: 310.39 g/mol
- Solubility: Insoluble in water; soluble in oils and organic solvents
- Log P: 4.19
Protection Spectrum
- Mechanism of Action: Absorbs UVA rays and converts them to heat
- UVB Protection: Low (<50%)
- UVA I Protection: High (>85%)
- UVA II Protection: High (>85%)
- HEV/Blue Light Protection: Moderate (50–85%)
Side Effects and Safety Profile
- Skin Reactions: Rare cases of contact dermatitis and photosensitivity have been reported, though avobenzone is generally considered a weak sensitizer.
- Photodegradation: Breakdown products from UV exposure can contribute to instability and may increase oxidative stress unless stabilized.
- Endocrine Activity: Some in vitro studies have suggested potential estrogenic effects, but regulatory reviews including the EU Scientific Committee have not confirmed any risk to human health from typical topical use.
- FDA GRASE Classification: Non-GRASE (Category III)
Regulatory Status
- United States: Approved for use in sunscreens at concentrations up to 3%
- European Union: Approved up to 5%
- Japan and other regions: Similar use permitted, often with more advanced stabilization systems allowed in formulations
Photostability Challenges and Nanotechnology Approaches
Avobenzone’s photoinstability is a major formulation concern. Studies have shown that when paired with octyl methoxycinnamate, its degradation is worsened. In contrast, combining it with broad-spectrum filters like Tinosorb S improves stability.
Recent innovations include encapsulating avobenzone in nanostructured carriers, such as:
- Mesoporous silica microparticles, which reduce avobenzone’s skin penetration and slow photodegradation
- Hybrid silica gels, which enhance surface area and stability while maintaining high UVA protection
- Organosilica nanocarriers, offering a promising route for creating photostable, non-irritating sunscreen formulations
These delivery systems reduce avobenzone’s interaction with other photoactive ingredients and with the skin itself, improving safety while maintaining efficacy.
