Homosalate (Homomenthyl salicylate)
What Is Homosalate?
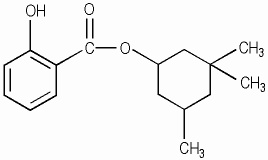
Homosalate is an oil-soluble chemical sunscreen filter from the salicylate family, commonly used to protect the skin from UVB radiation (295–315 nm). It appears on ingredient labels as homomenthyl salicylate or 3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexyl 2-hydroxybenzoate and is widely used in sunscreens and SPF-containing skincare products.
It functions primarily as a UVB absorber, helping prevent sunburn and DNA damage. Homosalate is a liquid at room temperature, which makes it particularly useful for dissolving other sunscreen agents like avobenzone in oil-based formulations. However, it is not a strong UV filter on its own and must be combined with other ingredients for full-spectrum protection.
How It Works
Homosalate absorbs UVB rays and converts the energy into heat, thereby reducing their ability to cause skin damage. Although it offers moderate UVB protection, it does not protect against UVA rays. It is also not photostable, and can lose about 10% of its protective ability within 45 minutes of sun exposure. For this reason, it is commonly used in combination with more stable filters and antioxidants to support overall sunscreen performance.
Key Specifications
- Structure: C₁₆H₂₆O₃
- Chemical Class: Salicylates
- IUPAC Name: 3,3,5-trimethylcyclohexyl 2-hydroxybenzoate
- Molecular Weight: 266.38 g/mol
- Solubility: Insoluble in water; soluble in oils and alcohols
Protection Spectrum
- Mechanism of Action: Absorbs UVB rays and converts them to heat
- UVB Protection: Moderate (50–85%)
- UVA I Protection: Low (<50%)
- UVA II Protection: Low (<50%)
- HEV/Blue Light Protection: Low (<50%)
Side Effects and Safety Profile
Homosalate is generally well tolerated, but several in vitro studies suggest it may have endocrine-disrupting potential. It has been shown to act on estrogen, androgen, and progesterone receptors, promoting the growth of hormone-sensitive cells. It has also been detected in human breast milk, raising concerns about exposure during pregnancy and infancy.
Another safety concern is its ability to enhance skin penetration—homosalate can increase the absorption of other chemicals, including certain pesticides, through the skin barrier. While these findings are mostly from lab or animal studies, they have prompted a closer review of its use in personal care products.
FDA GRASE Classification
-
Classification: Non-GRASE (Category III) — Additional safety data required
Regulatory Status
- United States: Approved for use in sunscreens up to 15%
- European Union: Approved with similar concentration limits
- Japan: Permitted under standard regulations
